Ace Game Engines These are software structures designed primarily for the development of video games. They include relevant libraries and support programs, such as level editors. Also, the game engines or game engines offer tools to create games on consoles and other types of computers.
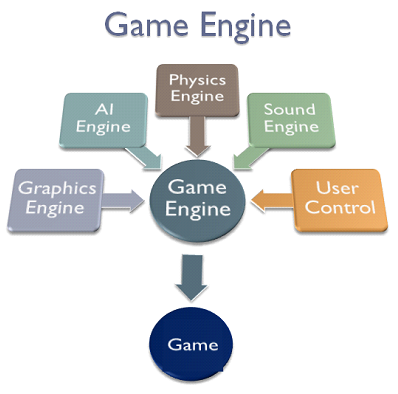
The main components of a game engine include:
- Rendering: for 2D or 3D graphics.
- Physics: Collision detection and response.
- We are: for sound effects and sound tricks.
- Scripting: for game logic programming.
- Artificial intelligence: to control characters who are not jogáveis.
- Network: for multiplayer support.
- Memory management, among others.
History of Game Engines:
Before two game engines, games were generally developed as singular entities, without separation from areas such as graphics and physics. The rapid advancement of hardware results in the need to discard old codes and adopt different designs to take advantage of new technologies.
The term "game engine" emerged in the 1990s, especially with 3D games such as Doom and Quake. Developers are beginning to license cores of these games to create their own engines. Over time, game engines have also been used in game development, being used in training, medicine and military simulations.
Embora or thermos gained popularity in the 1990s, with some systems in the 1980s, such as Sierra's AGI and SCI, LucasArts' SCUMM, and Incentive Software's Freescape Engine, also considered gaming engines. However, these older engines are rarely used by third parties, except for the SCUMM System, licensed to Humongous Entertainment. The first 3D engine used to create computer games was the Freescape Engine in 1986.
The emergence of APIs such as DirectX and OpenGL has driven the evolution of gaming technologies. DirectX, launched in 1995, replaced DCI and WinG, allowing the incorporation of high-performance multimedia in Windows. Although OpenGL was created first, DirectX gained more oil in the game development area.
Initially, companies built their own gaming engines, but as costs increased, some began to specialize in building engines to sell. Modern game engines are complex, with clear separation between rendering, scripting, art and snow design. Recent developments focus on efficiency, with high-performance programming languages such as C#, Java and Python becoming more common due to the increasing power of GPUs and PPUs.
List of Game Engines:
Here are some game engines you'll notice:
- Unity: Popular with independent developers. It supports several platforms and is free for minor projects 5.
- Unreal Engine: Widely used, with support for more than 25 platforms 4. Possess advanced rendering, physics and animation resources.
- Godot: Open-source and easy to use 4.
- Amazon Lumberyard: integrates with Amazon services 4.
- CryEngine: Made by impressive graphics 4.
Applications besides games:
As game engines have applications in both games:
- Military and medical simulations: training and planning.
- Films and TV: pre-production, scenes and visual effects.
- Architecture and Engineering: Detailed modeling of buildings and internal systems.
- Education: development of training and simulations.
- Advertising and Marketing: interactive visualizations.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: immersive experiences.
Unity Game Engine
Strong points:
- Wide compatibility: Supports more than 25 platforms.
- Ideal for beginners: free for basic projects.
- Easy to use: visual and intuitive.
- Broad audience: globally recognized.
- Fast and agile: transform ideas into reality quickly 5.
- Training platform: In Unity Learn, beginners have access to several free training courses ranging from basic to professional with specialization in programming, etc.
In short, game engines use tools that can also play games, impacting areas such as architecture, cinema and education. Unity is an excellent choice, especially for beginners and smaller projects.
Talk to me Software.com.br and knew more about Game Engines together with a specialist, via e-mail comercial@software.com.br.
See more about Game Engines na Software.com.br









 4 min reading
4 min reading




